CUTE REVISION NOTES
A) Formulas to remember:
1) Unit Price
Unit Price = Amount/UnitsUnits = Amount/Unit Price
Amount = Unit Price x Units
How to Remember?
Remember 1 formula and deduce the other 2.
Unit Price = $ divide units = RM per unit
Units number must be bigger than amount number when unit price is less than RM1.
Eg.
4000 units = RM1,000 / RM0.25
4000 (Units) > 1000 (Ringgit)
2) Raw Return (or Simple Return)
Simple Return = Future Value - Present Value
Present Value
or
Simple Return = End Value - Begin Value
Begin Value
or
Simple Return = new - old
old
Tips: "n" before "o"
3) Compounded Annual Return:
FV = PV(1+i)^n
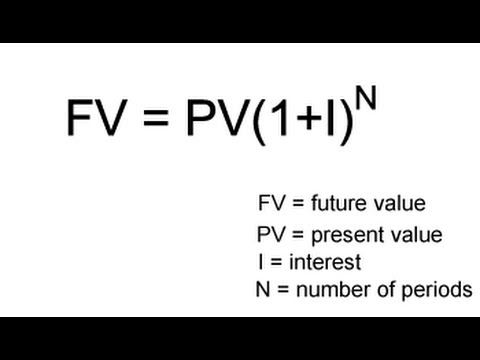
How to Remember?
Letter "F" comes before letter "P" in alphabets.
1 and I looks alike and must be added together like our eyes.
N sounds like "end" and must be at the "end".
How to use the Scientific Calculator to Calculator the Interest Rate.
4) LOAN
Max loan percentage = 67%.
How to Remember?
Bank only gives you maximum 2/3.
5) Portfolio Turnover Ratio (PTR)
PTR = 1/2 x [ total investment acquisitions + total investment disposal ]
Average Fund Size
How to Remember?
Average (buying + selling)
Average fund size
Note: 1/2 is the average
6) Management Expense Ratio (MER)
MER = [fees + recovered expenses] x 100%Average fund size
How to Remember?
Expenses percentage of fund
Notes: Average Fund Size appears both in PTR & MER at the bottom of the formula (the denominator).
7) Distribution
Investment Value (Total NAV) remains the SAME before & after DISTRIBUTION.Unit Price Decreased.
Units Increased.
New unit price = Unit Price - Distribution
cum-distribution = before distribution
ex-distribution = after distribution
8) Unit Split
Investment Value (Total NAV) remains the SAME before & after SPILT.Unit Price Decrease.
Units Increase.
Eg: Split 1:4
(Add 1 + 4 for total = 5)
New Unit Price = 4/5 x unit price
Unit Price Decrease (lower than previous unit price)
New Units = 5/4 x units
Units Increase (more than previous units number)
9) EPF Withdrawal
Account 1 = 70% x Total EPF
Max Withdrawal = (Account 1 - Basic Savings) x 30%
Eg. Total EPF = $100,000
Basic Saving = $40,000
Acc 1 = 70% x $100,000 = $70,000
Max withdrawal = (70,000 - 40,000) x 30% = $9,000
Minimum withdrawal is RM1, 000.00 per transaction.
Withdraw once every 3 months.
10) Taxation & Inflation
Return after tax = Investment return – (investment return x tax rate)Return after tax and inflation = Return after tax – inflation rate
Eg: Tax rate is 20%, Investment return is 10% and Inflation rate is 3%.
Return after Tax = 10% - (10% x 20%)
= 10% - 2%
= 8%
Return after Inflation = 8% - 3%
= 5%
11) Rule of 72
Double the money or Half the Purchasing Power.72/Rate = Years
72/Years = Rate
Eg: How many percent to double money in 8 years?
Rate = 72/8yr = 9%
12) Working Money
Actual money used for investment. Amount paid inclusive of initial service charge.Working Money = Investment Amount
(1 + Service Charge)
Note: Use working money to calculate Compounded return if Service charge is given in question.
B) Terms in Unit Trust
Forward Pricing
Unit price purchased or redeemed based on the price after the next valuation point. Normally, the price at the end of the day.
Deed
3 Parties to a deed:
1) Unit Holder
2) UTMC
3) Trustee
Institutions Involved
1) Securities Commission (https://www.sc.com.my)
2) FIMM - Federation of Investment Managers Malaysia (https://www.fimm.com.my)
Law
Capital Markets and Services Act 2007 (CMSA 2007)
REITs
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REIT) mainly invests in property. Derives rental income and capital appreciation of the properties.
ETF
Exchange Traded Funds generally hold all the companies on a big benchmark index and trade on the stock exchange as a single share.
Collective Investment Schemes
Investors with similar investment objectives to pool their money and invested into a portfolio of securities managed by investment professionals.
Open End Funds (like Unit Trust)
1) Units are NOT quoted on a stock exchange.
2) Unit prices are computed based on the underlying Net Asset Value of the Fund.
3) Prices remain same within the same trading day.
4) Size of fund would increase with creation of units and decrease with the cancellation of units.
5) Transacted directly with UTMC.
Close End Funds (like Stocks)
1) Units quoted and traded on stock exchange.
2) Prices determined by market forces of demand & supply.
3) Prices fluctuate throughout the day and from time to time.
4) Size of fund remains same until the next public issue.
5) Investors can only sell their units through the exchange.
Switching
Redeem from one fund & invest into another fund/funds.
Syariah Based UTS
Syariah-non compliance risk
When a Syariah-compliant security is reclassified as a Syariah-non compliant security.
Syariah Advisory Council of the Securities Commission will revise companies compliance every six months (last Friday of April and October) every year.
Unit Trust Syariah Contracts
Musyarakah contract - Between the unitholders to deal with specified investments, with the view that the profit derived would be shared among them according to capital contribution or any other agreed profit-sharing ratio.
Bai means the contract of sale and purchase executed between the unitholders and the UTMC.
Before Units Creation (Money is with UTMC)
Wakalah (agency) contract - UTMC act for and on behalf of the unitholders to invest and manage the UTS.
Wadiah Yad-Dhamanah (guaranteed custody) The owners of the units are the Unitholders; the custodian is the UTMC. The contract will take place when UTMC receives payment for the investment.
After Units Creation (Money is with Trustee)
Wakalah (agency) contract - Trustee act for and on behalf of the unitholders to be the custodian of the trust funds and to safeguard the interests of unitholders.
Wadiah Yad-Dhamanah (guaranteed custody). The owners of the units are the Unitholders; the custodian is the Trustee. The contract between unitholders and trustee exists once the money is deposited with the trustee and units are created.
How to Remember?
Musyarakah = Masyarakat (Community of investors)Wakalah = Wakil (Agent representative)
Wadiah Yad Dhamanah = Amanah (Trusted Custodian)
Bai = Buy
C) Other Notes
What is a Unit Trusts Scheme?
1) Collective investment2) investors with similar investment objective pool savings together
3) invest in portfolio of securities
4) managed by investment professionals
Benefits of Unit Trust
1) Diversification (different Asset Classes)2) Investment Exposure (different markets, regions)
3) Professional Management
4) Liquidity (access to funds)
5) Ease of Transaction
6) Investment Cost (low cost)
7) Dollar Cost Averaging (regular)
Disadvantages of Unit Trust
1) Opportunity Cost2) Lost of Control
3) Risk
4) Fees & Charges
Unit Trust History in Malaysia
Started in 1959 with Malayan Unit Trust Ltd.1st Shariah compliant fund - 1993 by Arab-Malaysian Unit Trusts Bhd.
1st Islamic Bond fund - 2000 by RHB Islamic Bond Fund.
NAV of fund
NAV consists of:1) Value of all assets owned (equities, bond, money market)
2) Dividend, interest and coupon payments received.
Methods of Investing
1) Lump Sum2) Regular
3) Reinvest Income
Fund Objective
1) Capital Growth2) Income
3) Capital Growth & Income
Risk Level of Fund Types
Lowest to Highest Risks1) Money Market
2) Bond
3) Balanced
4) Equity
Equity are normally shares of companies.
Bond fund is also commonly known as Fixed Income fund.
Balanced fund has mixture of Equity and Bonds.
Money Market are for short term, mostly deposits in banks.
Unit Trust Funds issue 2 reports
1) Annual Report (at financial year end)2) Interim Report (6 months later)
Note: Interim report does not have Auditor's report.
Returns from Unit Trusts:
1) Distribution2) Capital Gain or Capital Appreciation
Capital Gain when Sell price higher than Buy price.
Capital Loss when Sell price lower than Buy price.
Distribution is received from Unit Trusts.
Distribution components:
1) Dividend received from Shares.2) Interest received from Money Market.
3) Coupon Payment received from Bond.
4) Realised Capital Gain from sales of assets.
Cooling off Rights
1) First time investor2) Except Corporate, UTC & Staff
3) Exercise (submit document) within 6 Business days
Repurchase
1) Money received within 10 Calendar days.Transfer
1) Change of UTS ownership from one person to anotherChange of Terms Used
Old Term => New TermFMUTM => FIMM
PDUT => UTC
You can watch videos to prepare for your CUTE Exam with this link:
http://highlevelrules.blogspot.com/p/cute-videos.html
You can download the full FIMM CUTE Exam e-Study guide from this link:








No comments:
Post a Comment